|
|
You think intestinal disorders don't matter? According to the latest research of scientistsIssuing time:2020-10-24 11:30 What do you know about the human intestines? The human intestine is about 7-8 meters long, and the total area after unfolding is about 200 square meters; there are more than 10 trillion intestinal flora in the intestine, weighing 1 kg... As the body's largest immune organ, the intestine is vital to human health. ↓↓↓  With the deepening of the understanding of the function of intestinal flora, more and more scholars are focusing on the relationship between disease and intestinal flora. Recently, an article named Gut microbiota metabolites as integral mediators in cardiovascular diseases was published in "INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MOLECULAR MEDICINE". The article focuses on the impact of intestinal flora metabolites on cardiovascular diseases, and thus develops the most economical and effective treatment for cardiovascular diseases with minimal side effects. 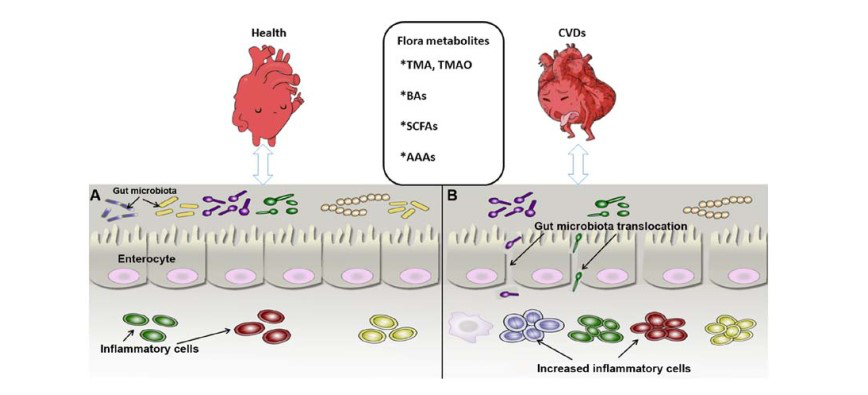 The relationship between intestinal flora metabolites and cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases Specifically, cardiovascular disease is usually accompanied by the imbalance and abundance of the intestinal flora. Intestinal flora metabolites such as trimethylamine (TMA), trimethylamine oxide (TMAO), bile acids (BAs), short-chain Fatty acids (SCFAs) and aromatic amino acids (AAAs) can regulate the occurrence of cardiovascular diseases through signal pathways such as inflammation and apoptosis. In a healthy state, the number of intestinal microorganisms is stable, inflammatory cells maintain normal defense functions, and intestinal epithelial cells are tightly arranged to form a mucosal barrier. When there is cardiovascular disease, the number of intestinal microbes is significantly reduced, and the permeability of intestinal epithelium increases, leading to translocation of intestinal flora, proliferation of inflammatory cells, and damage to the intestinal mucosa. 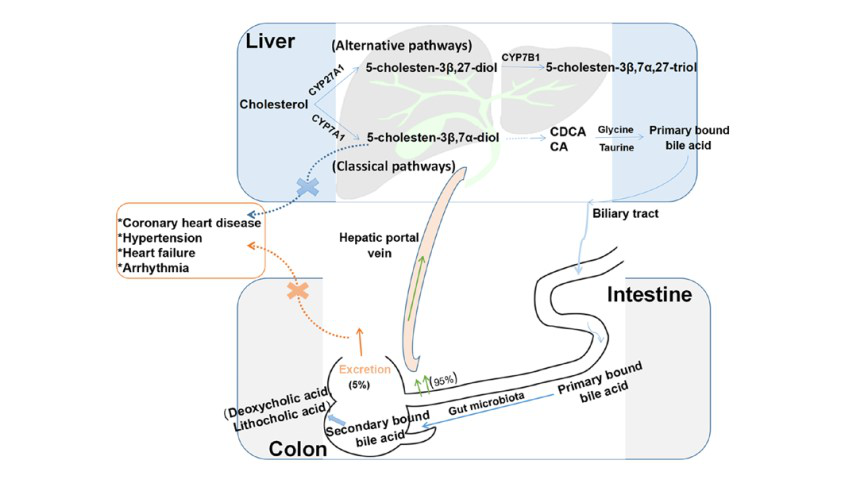 Hepatoenteric circulation of BAs The article focuses on the relationship between bile acids (BAs), short-chain fatty acids (ScFAs) and aromatic amino acids (AAAs), which are metabolites of intestinal flora, and cardiovascular diseases. Simply put, BAs can inhibit the abnormal proliferation of intestinal flora by acting on the farnesoid X receptor (FXR), regulate the expression of BcL-2/BAX, and cause cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Maintain stable blood pressure by regulating cortisol and aldosterone levels. In addition, hydrophilic BAs and the main ions inside and outside the cell membrane have anti-arrhythmic effects, and lipophilic BAs cause arrhythmia through changes in cell membrane potential. 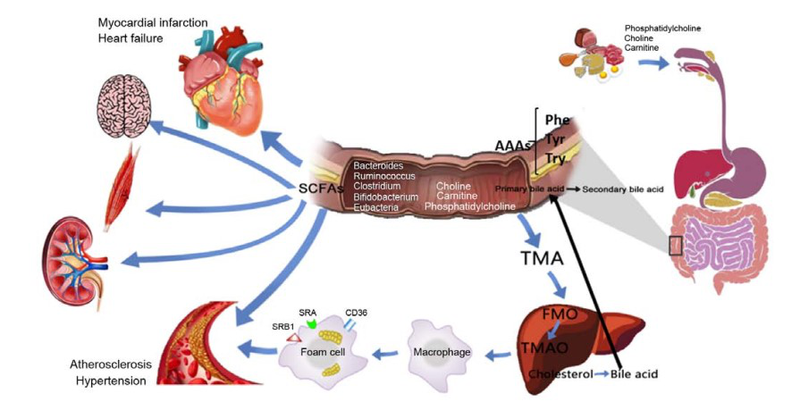 The role and mechanism of intestinal flora metabolites in cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases ScFAs can enhance Foxp3 histone acetylation by inhibiting HDAC, promote the differentiation of T cells into effector T cells and regulatory T cells, and inhibit inflammation. When AAAs undergo nitration, halogenation, sulfonation, alkylation and acylation reactions through GPRs, they can produce substances that damage the myocardium and vascular endothelium, and promote the occurrence of cardiovascular diseases. Based on the above-mentioned relationship between intestinal flora metabolites and cardiovascular diseases, the article also proposes several treatment methods. 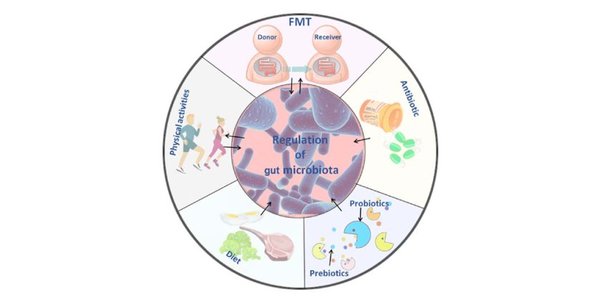 Cardiovascular disease treatment method based on metabolites of intestinal flora The daughter does not change her health, she must pay attention to her diet, work and rest, and maintain proper exercise to keep her intestines healthy and healthy! |

