|
|
Why can some people regulate their emotions reasonably and effectively? But some people can't?Issuing time:2020-10-24 10:46 Imagine the following scenario. When a busy day is coming to an end, comments from your boss may make you impatient. You may blush and want to refute, but at this time you will also stop to reflect and choose not to express this. This kind of dissatisfaction; this scene fully demonstrates how humans regulate their emotions. Our control of emotions is not limited to suppressing outbursts of anger, which means that we can control our emotions well, and how and when these emotions are expressed and experienced. Effective control of emotions allows us to maintain a positive attitude in times of difficulty or pretend to be happy when opening a bad birthday present. Effective control of emotions will allow us to enjoy positive emotions more and experience negative emotions less. Therefore, controlling emotions is very important to the health of the organism. On the contrary, emotional disorders are directly related to mental health conditions and mental illnesses, such as emotion regulation. Strategy disruption is often considered to play a key role in the occurrence of many diseases, such as depression, anxiety, drug abuse, and personality disorders.
How to effectively manage your own emotions? In its essence, emotions can make us smell and feel, and also make us start to act. This is due to changes in the body's autonomic nervous system and endocrine system. It can participate in and support emotion-related body behaviors, such as In fear, adrenaline can be secreted to help the body escape danger. Before emotions occur, a situation will appear first. This situation may be external or internal. Simply put, this situation is evaluated according to its meaning to us, and it will cause the body to feel emotionally. Some reactions.
Image Source:courses.lumenlearning.com Psychologist James Gross described five strategies to help regulate the body’s emotions, which can also be used at different stages of the emotion generation process; these five strategies include: 1) Situation selection This includes looking to the future and taking measures to make it more likely to have satisfactory emotions, or less likely to cause bad emotions, such as taking a longer but quieter route home from get off work to avoid rage. 2) Situation modification (Situation modification) This strategy can be implemented when we are already in a certain situation. It refers to measures taken to change or improve the emotional impact of this situation, such as seeking common ground while reserving differences when the conversation becomes intense. 3) Attentional deployment Have you ever been distracted to face fear? This is a distribution of attention that can be used to guide or focus attention in different aspects of the situation. For example, people who are afraid of needles can recall things that make them happy when they draw blood. 4) Cognitive change This is about changing the way we evaluate things to change how we feel about things. A special form of cognitive change is re-evaluation, which involves different ways of thinking or considering more positive aspects, such as re-evaluating what is lost. Work is an exciting opportunity to try new things. 5) Response modulation (Response modulation) Response adjustment usually occurs in the later stages of the emotional production process, including changing our reactions or expressing our emotions to reduce or increase emotional impact, such as hiding anger towards colleagues.
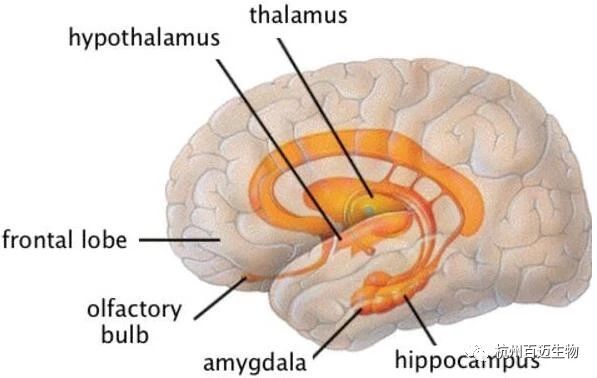
How does the brain do it? The molecular mechanisms behind the above strategies are not the same and extremely complex. They involve psychological, cognitive, and biological processes. The cognitive control of emotions involves the cerebral cortical emotional system (midbrain periaqueductal gray matter, hypothalamus and The interaction between the amygdala) and the cognitive control system of the prefrontal lobe and cingulate cortex. Take re-evaluation as an example (it is a strategy of cognitive change). When we re-evaluate, the cognitive control ability supported by the prefrontal cortex will change the contextual meaning to manage the body’s sensations, which will lead to the brain The activity of the emotional system under the deep cortex is reduced. Not only that, by lowering the heart rate and sweating response, it can also reassess and change the body's physiological functions, thereby improving our emotional experience. In other words, looking at the positive side does make us feel better, but not everyone can do it. Those with mood disorders (such as depression) have difficulty maintaining positive emotions in long-term emotional states. Studies have shown that depressed people show abnormal activation patterns in the same cognitive control area of the prefrontal cortex, that is, the more depressed these people are, the less able they are to adjust their own negative emotions with re-evaluation strategies. However, although some people may find it difficult to reassess, it may be easier to make situational choices, whether in nature, chatting with friends and family, lifting weights, hugging a dog, or doing something that makes you smile. Help you see a more positive side in life. The above content is reproduced from: Biological Valley. Image source: Internet If there is any infringement above, please contact us first, thank you. |